

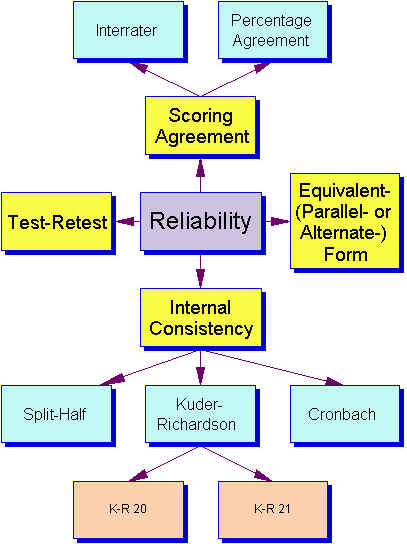
Standardized PTs can be appealing for many reasons. Several HEIs use commercial or standardized PTs for placing students in undergraduate programs, while many others design their own tests. Inaccurate placement may have financial implications, impact students’ degree plans, and lead to an adverse impact on their motivation levels ( Hille and Cho 2020). In addition, the teaching and learning process can be a struggle for both teachers and students when students are misplaced ( Johnson and Riazi 2017). An invalid and unreliable test tends to place students at the wrong levels, which may have an adverse impact on the student’s proficiency and develop negative attitudes towards the university among students ( Al-Adawi and Al-Balushi 2016). However, the effectiveness of such tests in placing students into appropriate levels is often questioned as they might suffer from validity and reliability issues ( Fan and Jin 2020). 2015) and are cost-effective ( Jamieson et al. It is believed that in-house tests ensure a range of benefits as they are customized to the specific curricular goals of the academic programs offered by the institutions ( Chung et al. The study offers useful insights to test developers and policymakers regarding the authentication of in-house tests and the creation of guidelines for PT design and evaluation.īased on the specific requirements and other academic considerations, higher Education institutions (HEIs) either use commercially available tests or develop in-house tests to place students into different levels of the FP. The data analysis revealed that the PT was effective in placing students at different levels of the foundation program (FP) and the statistical analyses conducted to test the reliability and validity showed positive results for most of the test versions. Paired sample t-test (dependent t-test) was used to assess the inter-rater reliability of the speaking and writing tests which were double-marked. The internal consistency and reliability of the reading test items were measured using Cronbach’s alpha while descriptive statistics were calculated for the listening test. New Student Survey was used to investigate the face validity. The content validity was established through the internal and external moderation of the question papers and answer keys while criterion-related concurrent validity was established via IELTS benchmarking. This study assesses the validity, reliability, and effectiveness of an in-house online PT. Although placing students in the appropriate proficiency levels of post-secondary English programs is crucial for optimal learning, the evaluation of placement tests (PTs) in terms of establishing their reliability and validity is relatively under-researched.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
